Describe the Structural Organization of the Genome
The extra DNA that accounts for differences in maize and sorghum genome size is mainly non coding repetitive sequence between genes. Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal.

Structural Genomics An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
DNA is a linear molecule.

. Similar to that prokaryotic genome is small and less complex compared to eukaryotic genome. For example a tumor can interrupt the function of the organ it is in despite the fact that it is a molecular mutation with direct cellular implications. Each DNA strand is about 18 meters long but squeezed into a space of 009 micrometers.
DNA stores all the information that makes up an organism. The principal difference between structural genomics and traditional structural prediction is that structural. At any of its three informational levels.
Structural genomics seeks to describe the 3-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by a given genome. Describe the two experiments that indicated that genes are made of DNA. I the chain of nucleosomes.
DNA is organized into chromosomes and all of the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA sequences from human chromosomes and chromosomes of other organisms are enabling a detailed look at the structure and organization of protein-coding information in the context of genomes as a wholeGroups of genes can now be examined in relation to broader landscape features such as the guanine plus. Draw a fully annotated diagram of the structure of a short DNA polynucleotide containing each of the four nucleotides.
Gene Structure and Organization In its simplest form a gene can be visualized as a seg-ment of a DNA molecule containing the code for the. The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid remember that prokaryotes do not have a separate membrane-bound nucleus. Base-pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine.
Escherichia coli is taken as model organism for the study of prokaryotic chromosomes because they are simple easily available easily grown in culture broth and less pathogenic. General Properties of DNA. Iii the mode of suprasolenoidal DNP-packing--loops or domains.
Normal diploid cells contain two copies of the nuclear genome and a much larger but variable number of copies of the mitochondrial genome. We begin by examining the structure of genes as a foundation for discussion of the genetic code transcription and translation. The phrase the human genome normally refers to the nuclear genome but should also include the mitochondrial genome.
Most of the information about the structure of DNA has come from studies of prokaryotes because they have simple structural organization compared to eukaryotes. The basic organization of the coronavirus genome is shared with other members of the Nidovirus order the torovirus genus also in the family Coronaviridae and members of the family Arteriviridae in that the nonstructural proteins involved in proteolytic processing genome replication and subgenomic mRNA synthesis transcription an estimated 14-16 end products. Eukaryotic genomes possess an elaborate and dynamic higher-order structure within the limiting confines of the cell nucleus.
DNA RNA or protein. One or a few circular or linear chromosomes Eukaryotes. DNA are made up of four building blockswhich are- cytosineC ThymineT Guanine G and adenineA.
Recent results bearing on the relation of these three levels to functional activity of. Tailed phages with double stranded DNA genomes vary in their size from 10 kbp to structure and gene assembly which encompass up to 15 kbp of the genome space. This genome-based approach allows for a high-throughput method of structure determination by a combination of experimental and modeling approaches.
FACTS ABOUT DNA. This clearly indicated that in most of the organisms only 1 of the DNA is utilized for protein production and rest may have a significant role in structure and organization of the genome. In prokaryotes the genome is composed of a single double-stranded DNA molecule in the form of a loop or circle Figure 1.
In its natural state each DNA molecule is actually composed of two single strands held together along their length with hydrogen bonds between the bases. Humans have two genomes nuclear and mitochondrial. Prokaryotes have a simple cell organization while eukaryotes have a complex cell organization.
Genome a cells endowment of DNA Hundreds to thousands of genes With interspersed controlling sequences Attached proteins control genes Chromosome structure Bacteria. Watson and Crick proposed that the DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix called a double helix. Ii the solenoidal or superbead nucleomere model of compactization of the nucleosomal fiber.
Knowledge of the physical principles and the molecular machinery that govern the 3D organization of this structure and its regulation are key to understanding the relationship between genome structure and function. Organized into functional units called chromosomes supercoiled DNA protein complexed of. Describe the structural organization of the genome Genome the total hereditary endowment of a cell.
Of the genome size 156 kbp are characterized by a long flexible non-contractile tail with a tape measure protein gene whose length corresponds to the phage tail. Structurally prokaryotic genome restricts to a single chromosome while eukaryotic genome has multiple chromosomes. One to 1000 linear chromosomes Present as decondensed chromatin between divisions Chromosome numbers.
Three levels of structural organization of eukaryotic DNA in the cell nucleus are considered in this paper. Indicate the changes that you would have to. Describe why cancer is a problem for the organism as a whole using your understanding of the levels of organization.
Cellular problems create issues at more complex levels of organization. 999 of DNA is identical in all humans on this Earth.

Structural Genomics An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Structure And Function Of The Bacterial Genome Wiley

Structure And Function Of Cellular Genomes Microbiology

The Genome Structure Function Evolution Structure Function Evolution Ppt Download

Genomic Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Structure And Function Of Cellular Genomes Microbiology

Simplified Illustration Of A Structural Genome Annotation Using Download Scientific Diagram

Beyond The Sequence Cellular Organization Of Genome Function Cell

Structural Genomics An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hierarchies Of Genome Organization The Hierarchical Process By Which Download Scientific Diagram

Phase Separation In Genome Organization Across Evolution Trends In Cell Biology

Difference Between Structural And Functional Genomics Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Genome Organization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Hcv Model Structure And Genome Organization Notes A Model Download Scientific Diagram

Hierarchies Of Genome Organization The Hierarchical Process By Which Download Scientific Diagram
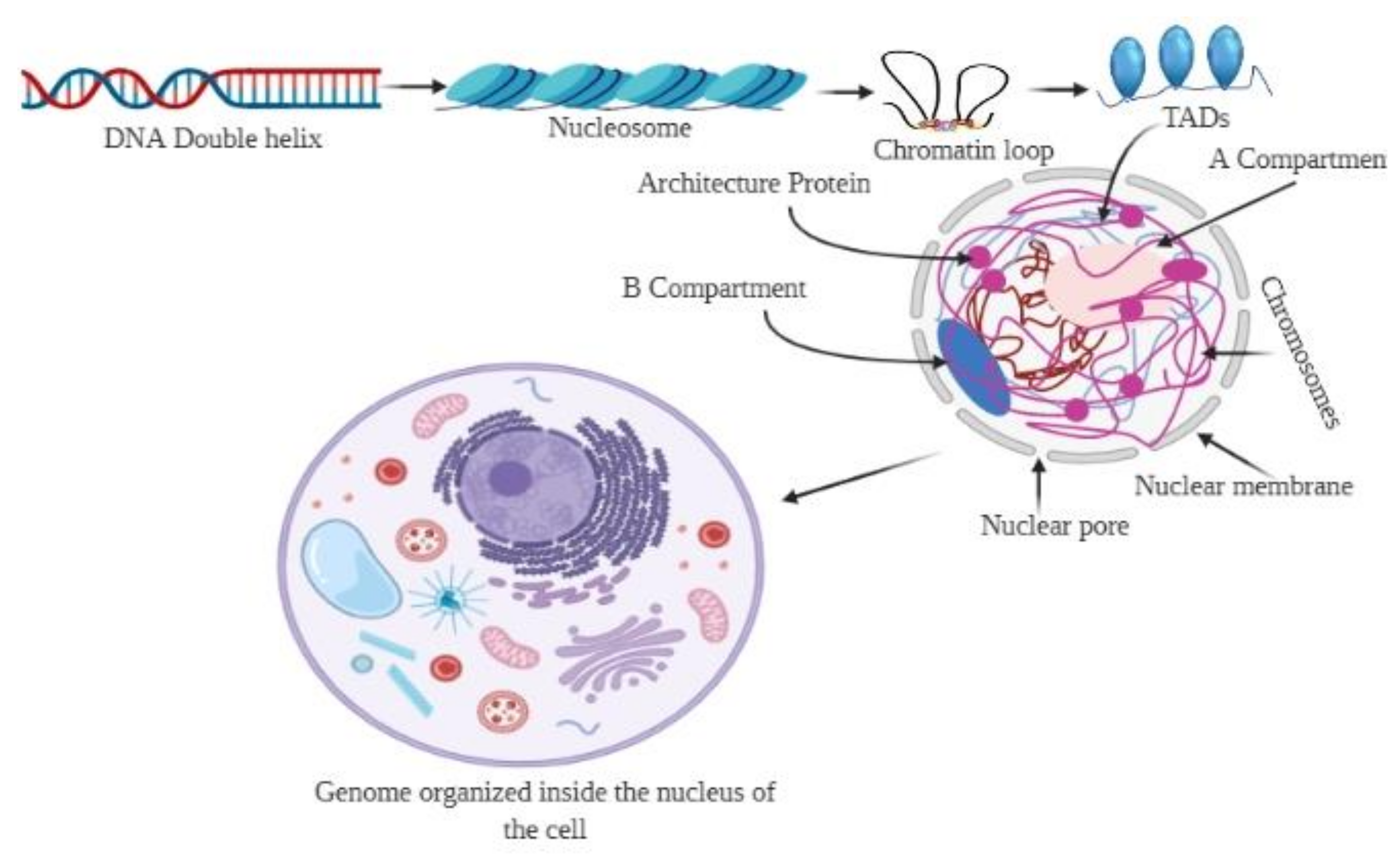
Ijms Free Full Text The 3d Genome From Structure To Function Html

The Role Of 3d Genome Organization In Development And Cell Differentiation Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology Cell Biology Genome Differentiation
Comments
Post a Comment